Problem
There is a directed weighted graph that consists of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1. The edges of the graph are initially represented by the given array edges where edges[i] = [fromi, toi, edgeCosti] meaning that there is an edge from fromi to toi with the cost edgeCosti.
Implement the Graph class:
Graph(int n, int[][] edges)initializes the object withnnodes and the given edges.addEdge(int[] edge)adds an edge to the list of edges whereedge = [from, to, edgeCost]. It is guaranteed that there is no edge between the two nodes before adding this one.int shortestPath(int node1, int node2)returns the minimum cost of a path fromnode1tonode2. If no path exists, return-1. The cost of a path is the sum of the costs of the edges in the path.
Example 1:
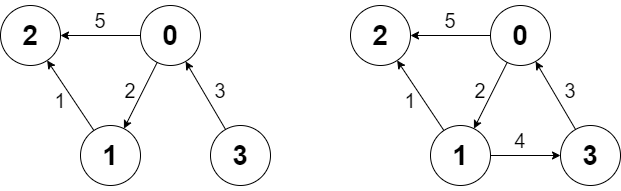
Input
["Graph", "shortestPath", "shortestPath", "addEdge", "shortestPath"]
[[4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]], [3, 2], [0, 3], [[1, 3, 4]], [0, 3]]
Output
[null, 6, -1, null, 6]
Explanation
Graph g = new Graph(4, [[0, 2, 5], [0, 1, 2], [1, 2, 1], [3, 0, 3]]);
g.shortestPath(3, 2); // return 6. The shortest path from 3 to 2 in the first diagram above is 3 -> 0 -> 1 -> 2 with a total cost of 3 + 2 + 1 = 6.
g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return -1. There is no path from 0 to 3.
g.addEdge([1, 3, 4]); // We add an edge from node 1 to node 3, and we get the second diagram above.
g.shortestPath(0, 3); // return 6. The shortest path from 0 to 3 now is 0 -> 1 -> 3 with a total cost of 2 + 4 = 6.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000 <= edges.length <= n * (n - 1)edges[i].length == edge.length == 30 <= fromi, toi, from, to, node1, node2 <= n - 11 <= edgeCosti, edgeCost <= 106There are no repeated edges and no self-loops in the graph at any point.
At most
100calls will be made foraddEdge.At most
100calls will be made forshortestPath.
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
*/
var Graph = function(n, edges) {
var map = Array(n).fill(0).map(() => []);
for (var i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
map[edges[i][0]].push([edges[i][1], edges[i][2]]);
}
this.map = map;
};
/**
* @param {number[]} edge
* @return {void}
*/
Graph.prototype.addEdge = function(edge) {
this.map[edge[0]].push([edge[1], edge[2]]);
};
/**
* @param {number} node1
* @param {number} node2
* @return {number}
*/
Graph.prototype.shortestPath = function(node1, node2) {
var visited = {};
var queue = new MinPriorityQueue();
queue.enqueue(node1, 0);
while (queue.size()) {
var { element, priority } = queue.dequeue();
if (element === node2) return priority;
if (visited[element]) continue;
visited[element] = true;
this.map[element].forEach(item => {
queue.enqueue(item[0], item[1] + priority);
});
}
return -1;
};
/**
* Your Graph object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new Graph(n, edges)
* obj.addEdge(edge)
* var param_2 = obj.shortestPath(node1,node2)
*/
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n * log(m)).
- Space complexity : O(n).