Problem
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return **the number of special positions in **mat.
A position (i, j) is called special if mat[i][j] == 1 and all other elements in row i and column j are 0 (rows and columns are 0-indexed).
Example 1:
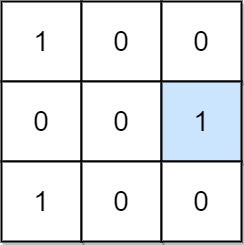
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[0,0,1],[1,0,0]]
Output: 1
Explanation: (1, 2) is a special position because mat[1][2] == 1 and all other elements in row 1 and column 2 are 0.
Example 2:
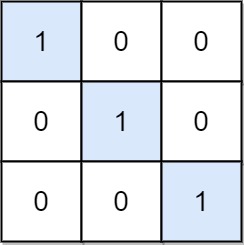
Input: mat = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation: (0, 0), (1, 1) and (2, 2) are special positions.
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 100mat[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution
/**
* @param {number[][]} mat
* @return {number}
*/
var numSpecial = function(mat) {
var res = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < mat.length; i++) {
var specialCol = -1;
var hasOnlyOne = false;
for (var j = 0; j < mat[i].length; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] === 1) {
if (specialCol === -1) {
specialCol = j;
hasOnlyOne = true;
} else {
hasOnlyOne = false;
}
}
}
if (!hasOnlyOne) continue;
var isValid = true;
for (var k = 0; k < mat.length; k++) {
if (mat[k][specialCol] === 1 && k !== i) {
isValid = false;
break;
}
}
if (isValid) res += 1;
}
return res;
};
Explain:
nope.
Complexity:
- Time complexity : O(n * m).
- Space complexity : O(1).